Creating a Forward Account¶
To create an account definition, follow the instructions below.
Click + icon next to the tab of the sub-section, or
Select > and then click .
Define object’s name.
Select Blocked option to disable account after it’s created (if needed).
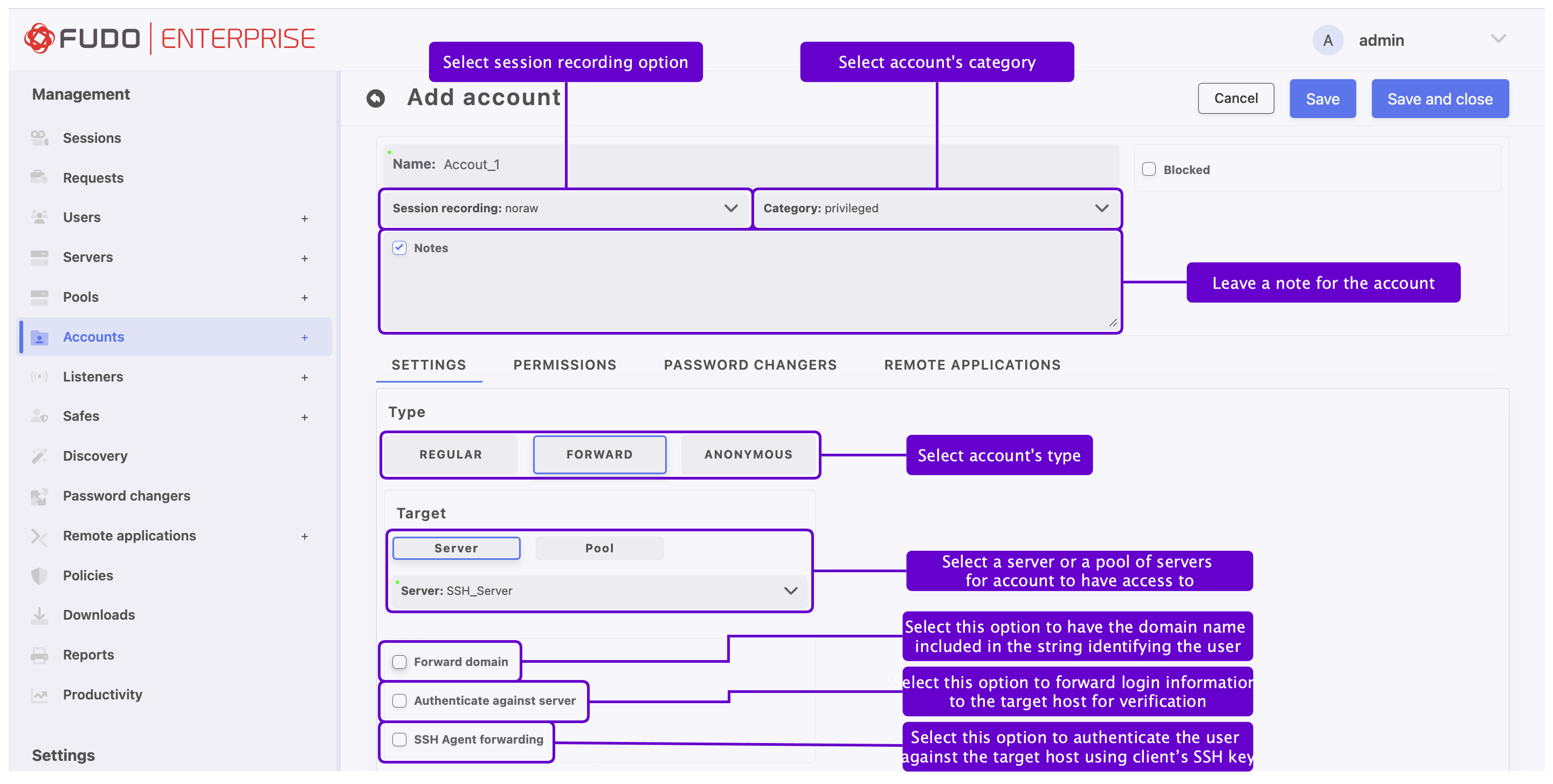
Select desired session recording option.
all- Fudo Enterprise saves session metadata (basic session information), records raw network traffic (RAW file) and stores session data in internal file format (FBS). The latter enables session playback using the built-in session player, as well as exporting sessions to a selection of video file formats.raw- Fudo Enterprise saves session metadata (basic session information) and records raw network traffic (RAW file). The raw data can be downloaded but it cannot be played back in graphical form using the built-in session player (session player only depicts the networks packet exchange between the client and the target host).noraw- Fudo Enterprise records the session data in a non-raw format that could be played back using the built-in session player.none- Fudo Enterprise saves only session metadata (basic session information).
From the Category drop-down list select
privilegedornon-privilegedaccount category.
Note
During manual account creation, assigning the category as privileged or non-privileged is purely informational, yet during the Discovery, it is automatically assigned based on the account’s parameters in the source system.
Select the Notes option to activate the field where you can enter a message for User Access Gateway users. If permissions are granted, notes can be also edited.
In the Settings tab, in the Type field, press the button.
In the Target section, select or button to assign account to a specific server or a server pool by selecting it in the next step from the Server, or Pool drop-down list.
Select Forward domain option to have the domain name included in the string identifying the user.
Note
- The Forward domain option utilizes user’s domain settings as follows:
If the user has an ‘AD Domain’ configured, Fudo Enterprise will use it for authentication againts the server.
If the user doesn’t have an ‘AD Domain’ configured but has a ‘Fudo Domain’ configured, Fudo Enterprise will use the ‘Fudo Domain’ for authentication against the server.
With the Authenticate against server option enabled, Fudo Enterprise does not verify the correctness of user credentials. Login information is forwarded to the target host, which verifies whether the user is allowed to access it. Verification status is returned to Fudo, which establishes monitored connection. To enable this authentication scenario, select the Authenticate against server option in the Credentials section (available only for SSH servers and RDP hosts with the Enhanced RDP Security (TLS) + NLA security option selected).
Note
Please note that 2FA/MFA authentication won’t work here. If you create a user with OATH+AD authentication the OATH part is bypassed and only the password is used and sent to the server – Fudo won’t ask for the OATH token in this situation. The same goes for Duo, SMS an any other 2FA user authentication scheme that can be configured in Fudo. This restriction is specific only to forward account types.
Select SSH Agent forwarding option to authenticate the user against the target host using client’s SSH key.
Note
This option is available only after selecting an SSH server. Use -A option for connecting to SSH server.
To have RDP, VNC or rendered HTTP sessions automatically processed, you can enable OCR session option for this account and select the language of processed data.
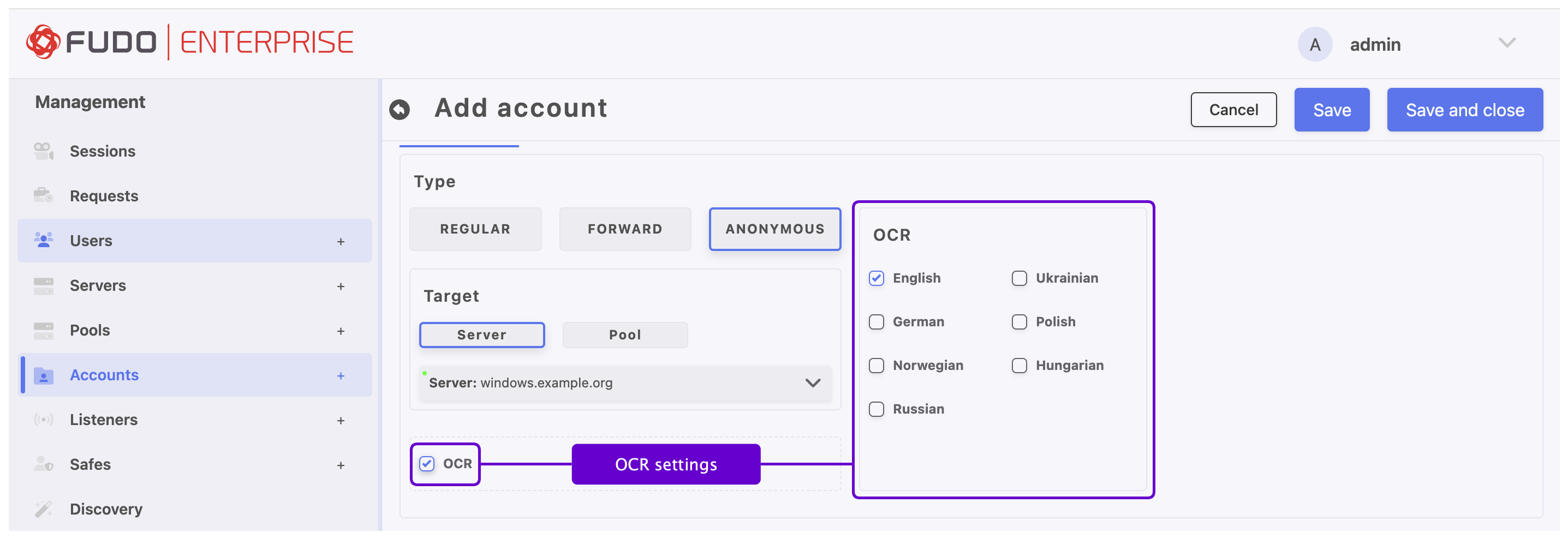
Note
The OCR option is available only after selecting an RDP, VNC or HTTP server.
In the Credentials section, enter privileged account domain.
Note
If a domain is entered in the Domain field, Fudo Enterprise will always use it to authenticate against the server. The domain will be added automatically to the user’s login.
In the Replace secret with section, click the button corresponding to one of the desired options.
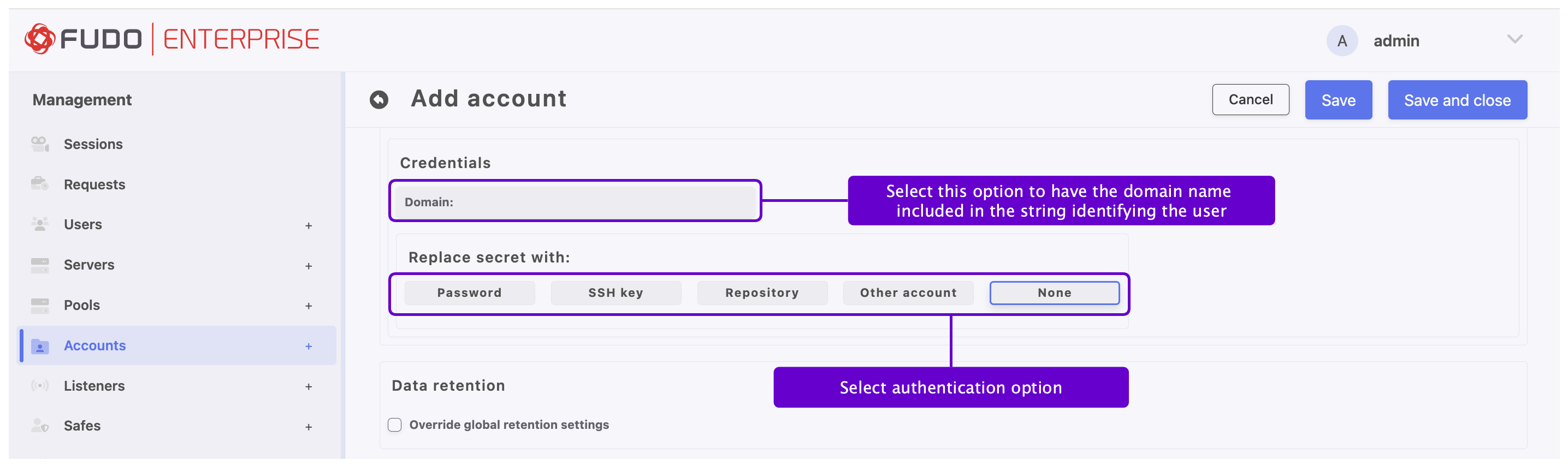
Provide account password in the Secret field.
Note
Two-fold authentication
With two-fold authentication enabled, user is being prompted twice for login credentials. Once for authenticating against Fudo Enterprise and once again for accessing target system.
To enable two-fold authentication, select Password from the Replace secret with section and leave the password and login fields empty.
Click the button and select the key algorithm.
Or click the button and browse the file system to find the key definition file. Provide the Key passphrase if needed for the uploaded file.
Select external repository name.
Note
To learn more about defining an external password repository, please refer to the External Passwords Repositories section.
From the Account drop-down list, select account object, whose credentials will be used to authenticate user when establishing connection with monitored server.
Note
The list contains only objects to which you have been given access permissions.
In this case no credentials will be forwarded.
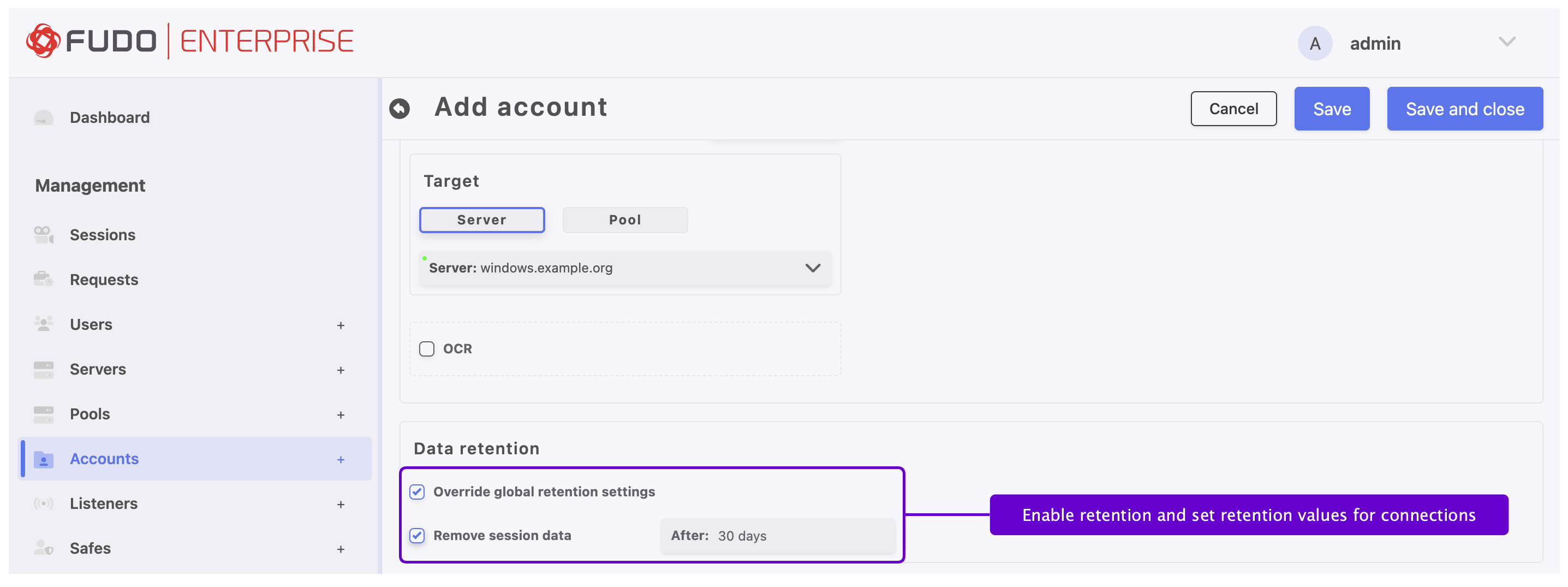
In the Data retention section, define automatic data removal settings.
Select Override global retention settings option to set other than global retention values for connections established using this account.
Check the Remove session data option to exclude sessions from retention mechanism.
Next to the Remove session data field, define the number of days after which the session data will moved to external storage device. Default value when the option is checked, is 30 days.
Go to the Permissions tab to add users allowed to manage this object.
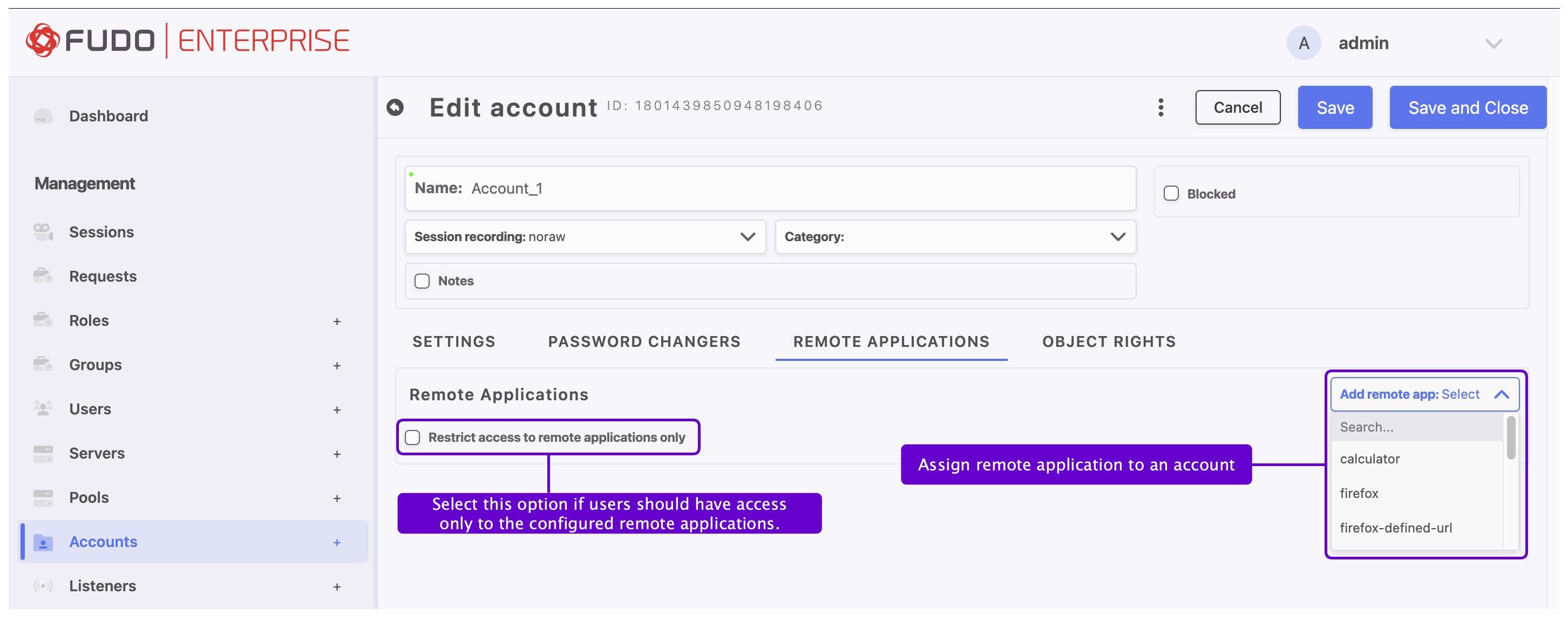
Go to the Remote applications tab to assign the desired remote application entries to an account, enabling direct RDP connections to those applications.
Note
To learn more about defining remote applications and restricting access to the full desktop, see the Remote Applications section.
Note
The Remote applications tab is active only when creating a regular or forward account with an RDP server or pool assigned.
The Password changers tab is active only when creating regular account types.
Related topics: