Creating an SSH listener¶
- Click + icon in the main menu next to the tab, or
Select > and then click .
- Enter listener’s unique name.
- Select Blocked option to disable access to servers through this listener after it’s created.
- Select the Case insensitivity option to disable case sensitivity in the username string when connecting over this listener.
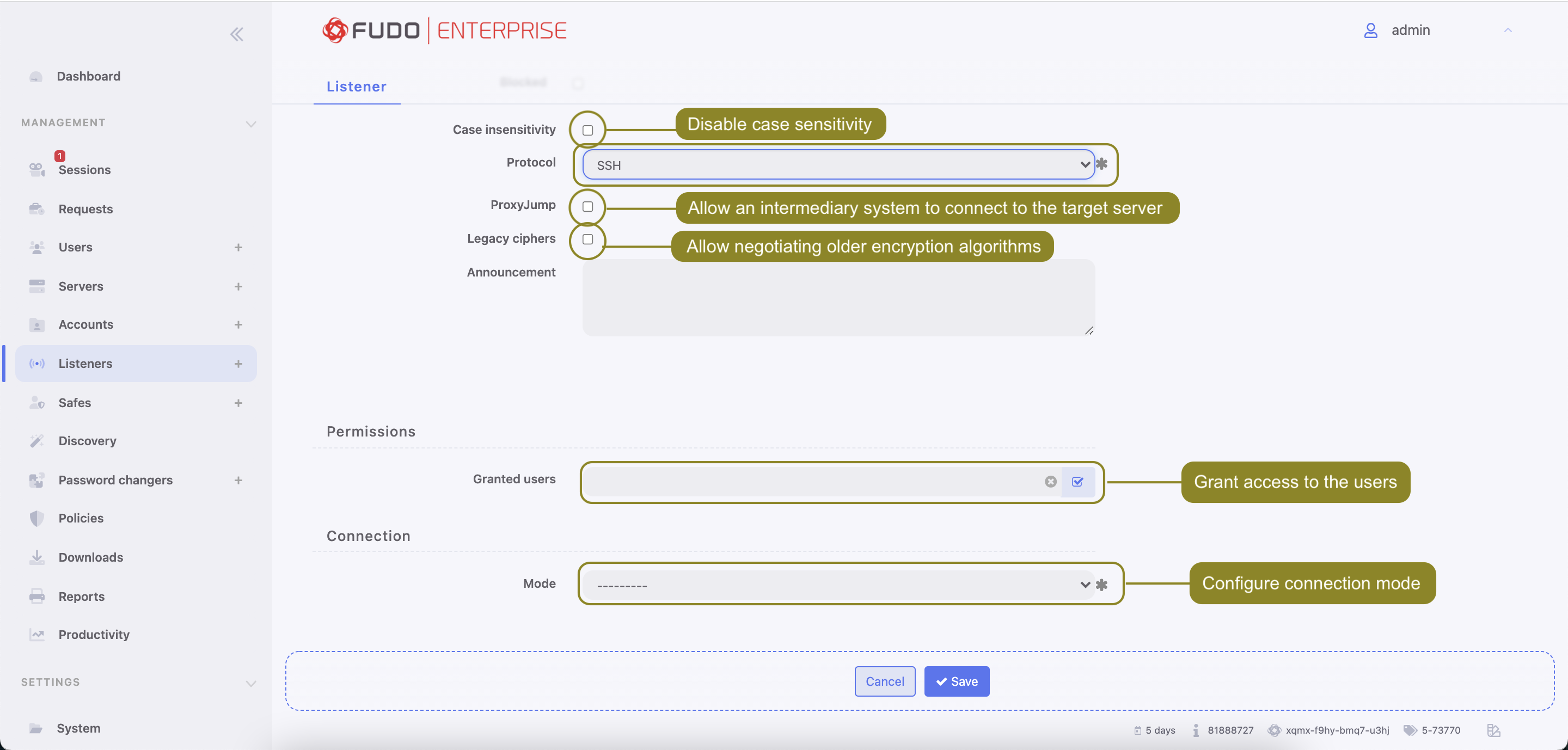
- Select
SSHfrom the Protocol drop-down list.
- Select ProxyJump option to allow an intermediary system to connect to the target server.
- Select Legacy ciphers option to allow negotiating older encryption algorithms (DSA(1024), RSA(1024)) when establishing SSH connections.
- In the Announcement field, type in the announcement that will be presented to the user on the login screen.
- In the Permissions section, add users allowed to manage this object.
- In the Connection section, select desired connection mode.
bastion
Note
- User connects to the target host by including its name in the login string, e.g.
john_smith#mail_server.- For details on bastion connection mode, refer to Connection modes topic.
Due to special interpretation of the
\character by different system shells (e.g. bash), user login and domain combination require specific formatting:
- “domain\user”#bsd01@10.0.60.138
- ‘domain\user’#bsd01@10.0.60.138
- domain\user#bsd01@10.0.60.138
- Select
bastionfrom the Mode drop-down list.- Select the the IP address from the Local address drop-down list and enter port number.
Note
- The Local address drop-down list elements are IP address defined in the Network configuration menu (Network interfaces configuration) or labeled IP addresses (Labeled IP addresses).
- Selecting the
Anyoption will result in Fudo listening on all configured IP addresses.- In case of cluster configuration, select a labeled IP address from the Local address drop-down list and make sure that other nodes have IP addresses assigned to this label. For more information refer to the Labeled IP addresses topic.
- In the External address field, enter an IP address (or FQDN name) along with the port number, under which Fudo can be accessed from outside the local network.
gateway
Note
User connects to the target host by providing its actual IP address. Fudo Enterprise moderates the connection with the remote host using own IP address. This option requires deploying Fudo Enterprise in the bridge mode.
- Select
gatewayfrom the Mode drop-down list.- Select the network interface used for handling connections over this listener.
proxy
Note
User connects to the target host by providing Fudo Enterprise IP address and port number which unambiguously identifies target host.
- Select
proxyfrom the Mode drop-down list.- Select the the IP address from the Local address drop-down list and enter port number.
Note
- The Local address drop-down list elements are IP address defined in the Network configuration menu (Network interfaces configuration) or labeled IP addresses (Labeled IP addresses).
- Selecting the
Anyoption will result in Fudo listening on all configured IP addresses.- In case of cluster configuration, select a labeled IP address from the Local address drop-down list and make sure that other nodes have IP addresses assigned to this label. For more information refer to the Labeled IP addresses topic.
- In the External address field, enter an IP address (or FQDN name) along with the port number, under which Fudo can be accessed from outside the local network.
transparent
Note
User connects to the target host by providing its actual IP address. Fudo Enterprise moderates the connection with the remote host using user’s IP address. This option requires deploying Fudo Enterprise in the bridge mode.
- Select
transparentfrom the Mode drop-down list.- Select the network interface used for handling connections over this listener.
- In the Fudo public key field, click i to upload (optionally provide encryption passphrase) or i to generate TLS certificate.
- Click .
Related topics: